How to test CORS configuration locally
• 3 minute read
cors, python, akamai
Warning: This is a note, so don't expect much 😅!
How can you assert if a CORS configuration is configured correctly 🤔? Basically, you have the following options:
- You configure it according to the required context and then tell whoever asked you the task that it's done. The person tests it for you then 🤥.
- The same as above, but we test everything before informing anyone else.
I usually do the second. The first option tends to fail to work, especially at special moments (Murphy's law). Though time is important, if we spend some time testing the configuration by ourselves, we save time in the end. It works like unit tests. The straightforward approach is to use CURL. You just need to know how prelight request works. In this note, I'll explain a more complicated method that shows more possibilities. So, let's suppose we have the following CORS configuration:
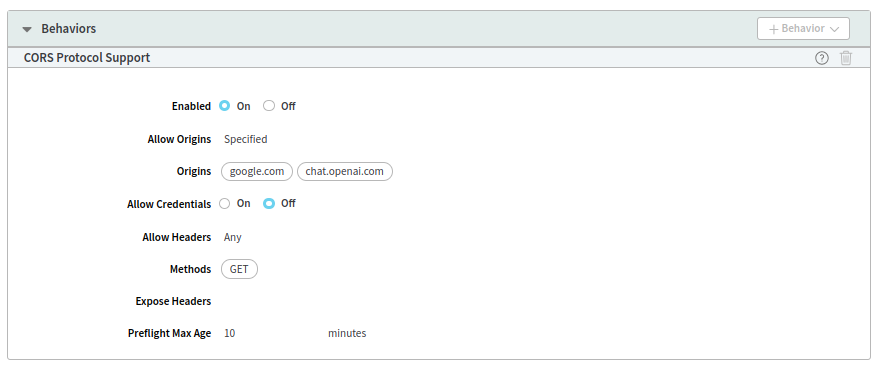
To test it locally, we can create the following Python script called server.py:
import http.server
import socketserver
import ssl
from pathlib import Path
context = ssl.SSLContext(ssl.PROTOCOL_TLS_SERVER)
print("Configuring context with a certificate")
context.load_cert_chain(Path("cert.pem"))
address = "0.0.0.0"
port = 443
print(f"Server address: {address}:{port}")
server_address = (address, port)
handler = http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
with socketserver.TCPServer(server_address, handler) as httpd:
httpd.socket = context.wrap_socket(httpd.socket, server_side=True)
print(f"Serving content from the current folder: {Path('.').absolute()}")
httpd.serve_forever()To serve through HTTPS, we need a certificate. Let's create one by using openssl:
openssl req -new -x509 -keyout cert.pem -out cert.pem -days 365 -nodesFor example, we can execute a GET in any resource to provoke the CORS configuration. So, let's create the following index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Sample test</h1>
<p id="output"></p>
<script>
const address = ""https://DOMAIN-THAT-HAS-CORS-CONFIGURATION/agrabah/jafar/lamp.json"
async function doIt() {
try {
const headers = {Pragma: "akamai-x-get-client-ip, akamai-x-cache-on, akamai-x-cache-remote-on, akamai-x-check-cacheable, akamai-x-get-cache-key, akamai-x-get-nonces, akamai-x-get-ssl-client-session-id, akamai-x-get-true-cache-key, akamai-x-serial-no, akamai-x-feo-trace, akamai-x-get-request-id, akamai-x-im-trace"}
const result = await fetch(address, {headers})
const body = await result.json()
console.log(body)
document.querySelector("#output").innerHTML = `The status code is ${result.status}`
} catch (e) {
document.querySelector("#output").innerHTML = `It failed! <strong>${e}</strong>`
}
}
doIt()
</script>
</body>
</html>You can add any Pragma headers you need to check other things beyond CORS, like cache configuration. Regarding Akamai, you may need to activate debug behavior in your property. Then, we can run the command:
sudo python3 server.pyWe have to use sudo to elevate the process to root because of port 443. Now, we are almost there! You should change /etc/hosts by adding the following lines:
127.0.0.1 google.com
127.0.0.1 chat.openai.comIf we access https://chat.openai.com/ or https://google.com/ the browser will say NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID. We can bypass it by proceeding.
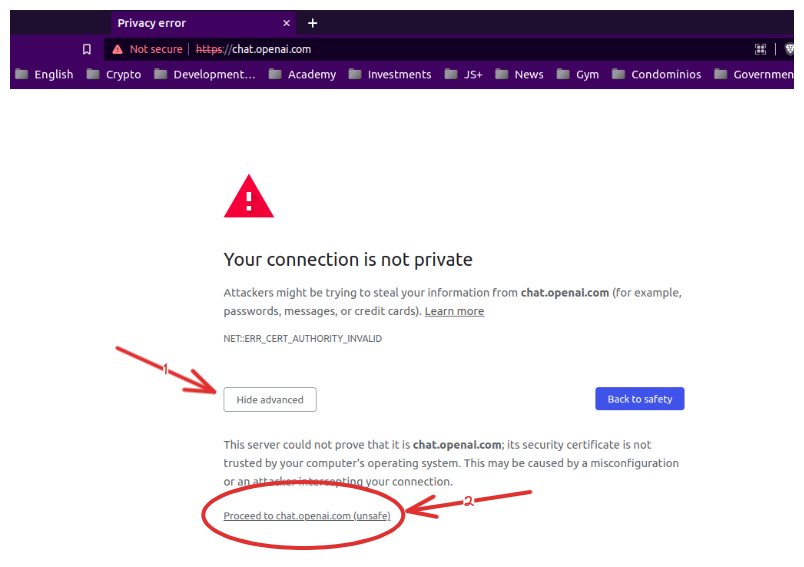
That's it! You are good to go 👍!
I hope this may help you. See you 😄!