Zero Dropped Connections during Ingress Pod Updates with AWS Load Balancer Controller
• 4 minute read
kubernetes, ingress, aws
Warning: This is a note, so don't expect much 😅!
Current environment:
- EKS 1.25
- AWS Load Balancer Controller v2.4.6 (Helm)
- NGINX Ingress Controller v1.8.0 (Helm)
I have been experiencing dropped connection while updating Ingress Controller pods. Many people are talking about the very same problem in issue 2366. So, to understand what was happening without impacting current services, I created a fresh Ingress Controller using the following recipe:
# helm install internal-nlb ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --namespace production -f ./internal-nlb-values.yaml --dry-run
# helm uninstall internal-nlb --namespace production
# helm upgrade internal-nlb ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --namespace production -f ./internal-nlb-values.yaml
# helm get values internal-nlb --namespace production
# https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-load-balancer-controller/v2.5/guide/service/annotations/
# https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/tree/main/charts/ingress-nginx
controller:
admissionWebhooks:
enabled: false
config:
http-snippet: |
# Rule to redirect HTTP to HTTPS using custom port 2443 (proxy_protocol). Know more at:
# https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/issues/5051
# https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/issues/9776
server {
listen 2443 proxy_protocol;
return 308 https://$host$request_uri;
}
use-proxy-protocol: "true"
containerPort:
http: 80
https: 443
redirect: 2443
electionID: internal-nlb
ingressClass: internal-nlb
ingressClassByName: true
ingressClassResource:
controllerValue: k8s.io/internal-nlb
default: false
enabled: true
name: internal-nlb
resources:
requests:
cpu: 15m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 172Mi
service:
# https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-load-balancer-controller/v2.2/guide/service/annotations/
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-additional-resource-tags: Environment=Production,Product=Cross
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-attributes: load_balancing.cross_zone.enabled=true
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol: http
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-proxy-protocol: '*'
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-scheme: internal
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-cert: arn:aws:acm:us-east-1:YOUR_ACCOUNT:certificate/YOUR_CERT_ID
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-ports: https
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-target-group-attributes: preserve_client_ip.enabled=true,proxy_protocol_v2.enabled=true
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-nlb-target-type: ip
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: external
targetPorts:
http: 2443
https: 80
watchIngressWithoutClass: false
replicaCount: 1Given the file name is internal-nlb-values.yaml, I issued the command:
helm install internal-nlb ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --namespace production -f ./internal-nlb-values.yamlThen I created a sample deployment that uses the ingress class above:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "false"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
name: sample-api-ingress
namespace: production
spec:
rules:
- host: test-sample-api.willianantunes.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: sample-api-service
port:
name: http-web-svc
path: /
pathType: Prefix
ingressClassName: internal-nlb
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
namespace: production
name: sample-api-service
spec:
selector:
app: sample-api
tier: web
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http-web-svc
protocol: TCP
port: 8080
targetPort: web-server
---
# After executing `kubectl proxy` you can issue:
# http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/production/services/sample-api-antunes-service:8080/proxy/health-check
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sample-api-deployment
namespace: production
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sample-api
tier: web
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sample-api
tier: web
spec:
containers:
- name: sample-api-container
image: willianantunes/runner-said-no-one-ever
ports:
- name: web-server
containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: PUMA_BIND_ADDRESS
value: "0.0.0.0"
- name: PUMA_BIND_PORT
value: "8080"
- name: RACK_ENV
value: production
- name: APP_ENV
value: production
- name: PUMA_MIN_THREADS
value: "4"
- name: PUMA_MAX_THREADS
value: "20"
- name: PUMA_NUMBER_OF_WORKERS
value: "1"
- name: PUMA_PERSISTENT_TIMEOUT
value: "20"
- name: PUMA_FIRST_DATA_TIMEOUT
value: "30"
- name: PROJECT_LOG_LEVEL
value: "DEBUG"
- name: RACK_IP_ADDRESS_HEADER
value: "REMOTE_ADDR"After creating it by executing kubectl apply -f sample-api-manifests.yaml, I was able to call the service by running the following:
curl --insecure -H "Host: test-sample-api.willianantunes.com" https://k8s-producti-internal-nlb-id.elb.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/health-checkMy environment was ready for a load test that would call the sample API indefinitely. To do that, I used JMeter. So while it was calling the API and asserting its result many times, I did the following scenarios:
- Change the requests for CPU.
- Decrease the number of replicas to 1.
- Change the limits for memory.
Each time the pod had to change, the error would increase:
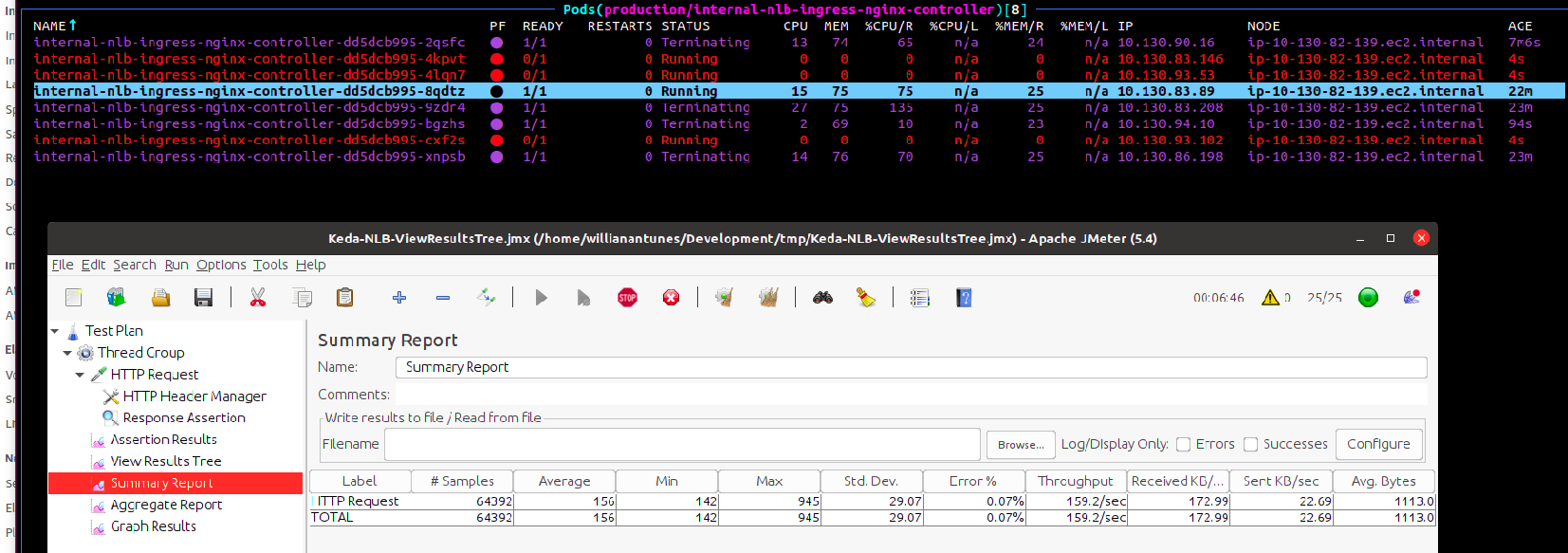
The NLB target group would also add new targets and drain the old ones, though the pods had already been terminated, which explains the error. While the target is draining, the NLB may send traffic for it still. To avoid errors, there is a workaround that uses container hook preStop and deregistration delay. Their value depends on your context, but let's say the following:
controller:
# ...
# ...
service:
annotations:
# ...
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-target-group-attributes: preserve_client_ip.enabled=true,proxy_protocol_v2.enabled=true,deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds=300
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command: [ "sleep", "420" ]Then I started a new test plan in JMeter and did the same scenarios above, but this time without downtime:
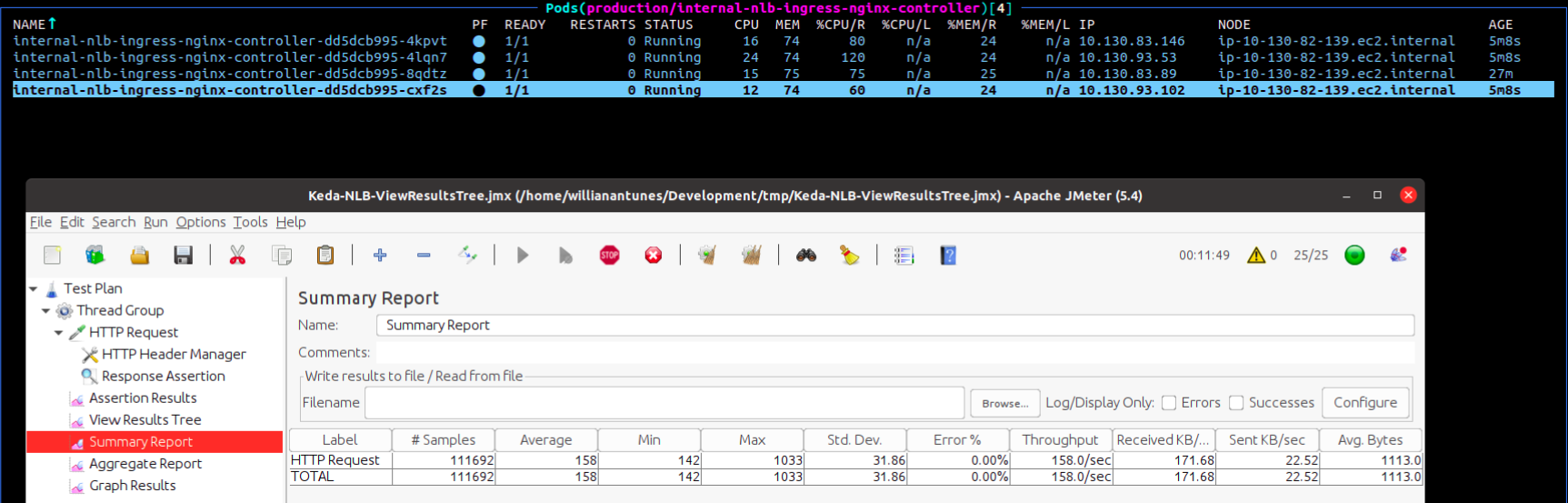
I hope this may help you. See you 😄!